A Comprehensive Guide to Lean vs. Six Sigma: Understanding the Differences
Lean’s Streamlined Efficiency Approach
Lean manufacturing was born from the Toyota Production System. Its roots lie in streamlining production to minimize unnecessary steps and resources. At its core, it is about doing more with less by systematically eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency. Key principles include value stream mapping, 5S methodology, and Kanban systems.
Lean can look like streamlining your warehouse operations, much like we discussed in our previous post, “Mastering Efficiency: Key Steps to Streamline Your Warehouse.”
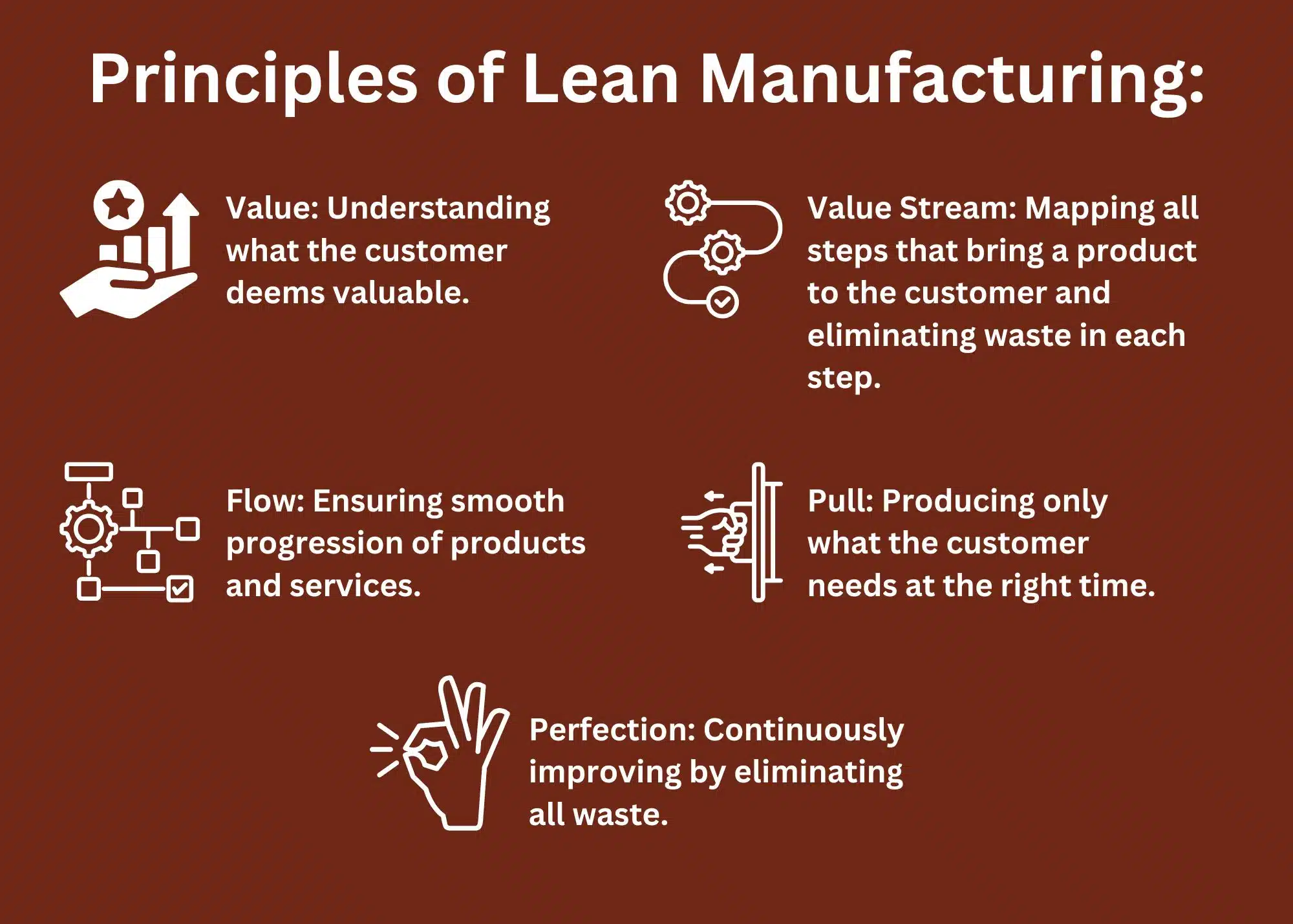
- Principles of Lean Manufacturing:
- Value: Understanding what the customer deems valuable.
- Value Stream: Mapping all steps that bring a product to the customer and eliminating waste in each step.
- Flow: Ensuring smooth progression of products and services.
- Pull: Producing only what the customer needs at the right time.
- Perfection: Continuously improving by eliminating all waste.
Lean’s approach is characterized by its agility in adapting to changes and maintaining productivity and quality with minimal resources. By maximizing value for the customer and minimizing waste, Lean transforms how products are built and delivered.
This philosophy resonates with our commitment to creating efficient and effective products like Trash Hoppers and Roll-Over Protective Structures (ROPS).
Six Sigma’s Data-Driven Quality Strategy
On the other hand, Six Sigma, originating at Motorola, revolves around improving quality by removing defects and variations in processes. It’s data-driven and relies heavily on statistical analysis and process measurement to foster a culture of quality that permeates the organization.
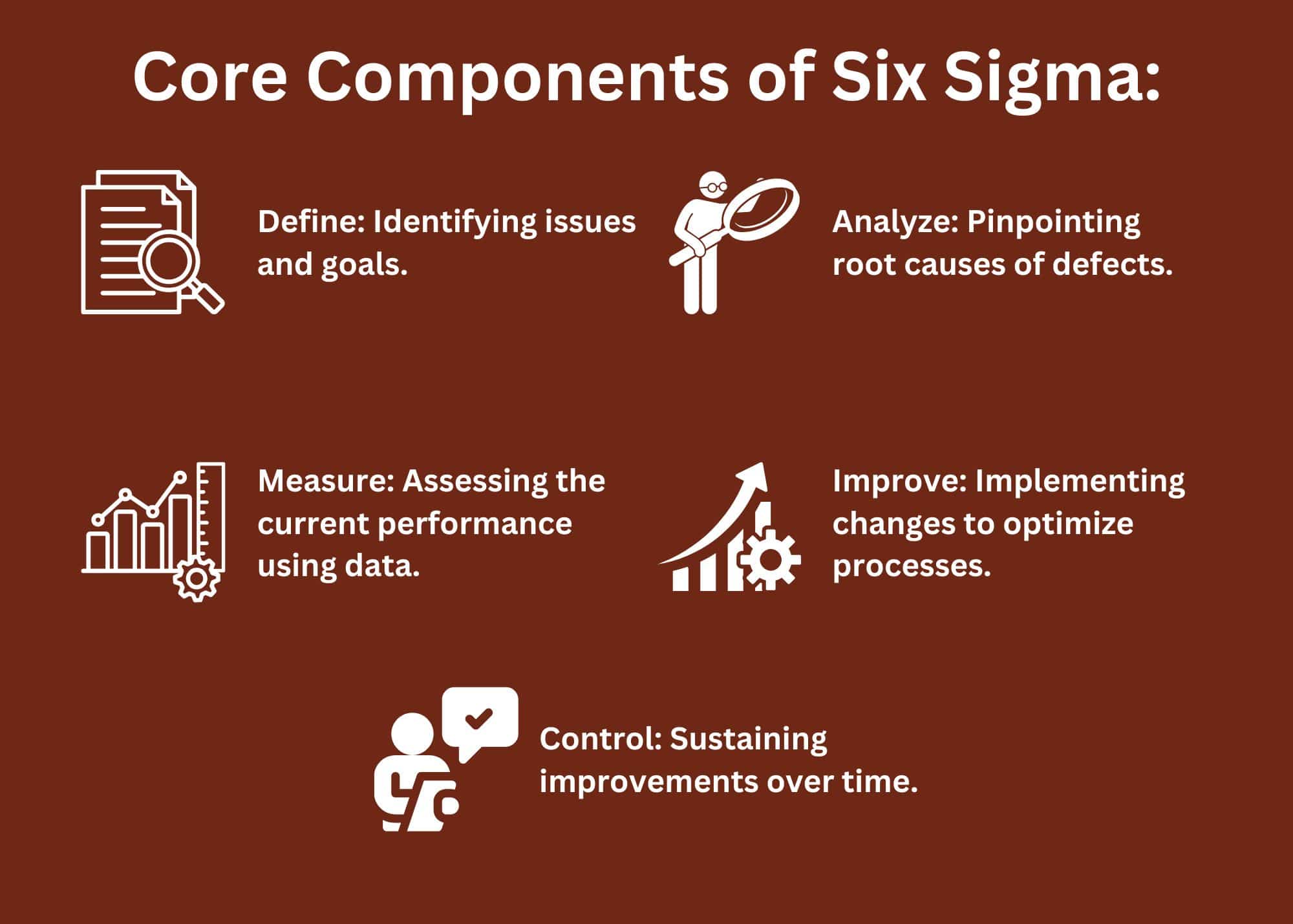
- Core Components of Six Sigma:
- Define: Identifying issues and goals.
- Measure: Assessing the current performance using data.
- Analyze: Pinpointing root causes of defects.
- Improve: Implementing changes to optimize processes.
- Control: Sustaining improvements over time.
Six Sigma’s model especially benefits manufacturers looking to enhance quality by reducing errors. This ensures products meet excellent standards every time.
This approach complements our dedication to creating robust products like the dumpsters and canopies we offer. For instance, Six Sigma principles directly impact the quality standards incorporated into our industrial trash hoppers. We anticipate and mitigate potential issues by meticulously analyzing production data. This guarantees our equipment meets the highest durability and safety standards. High-quality materials and precise manufacturing ensure you can depend on our products.

Comparing Benefits and Limitations
Both Lean and Six Sigma offer substantial benefits despite having different limitations.
Lean Benefits:
- Reduced Manufacturing Time: Simplified workflows and better resource allocation.
- Increased Flexibility: Adapt quickly to changes in demand. Easily implemented across diverse processes and industries.
- Cost Reductions: Minimized expenses by eliminating wasted resources.
Lean Limitations:
- Sometimes, detailed precision can be neglected because the focus is on speed and efficiency.
Six Sigma Benefits:
- Quality Improvements: Reduction in variation and defect rates.
- Predictable Processes: Extensive reliance on data ensures repeatable process quality.
- Customer Satisfaction: Higher quality results in happier customers.
Six Sigma Limitations:
- Requires significant investment in training and statistical education.
- Can be slower to produce immediate results due to meticulous analysis.
Both methodologies bring unique advantages and can be pivotal in achieving streamlined productivity and quality product delivery.
Choosing the Right Model for You
Determining the ideal approach requires a careful assessment of your business. What are your primary needs? Are you focused on improving speed or quality? What are your current processes? What are your long-term goals? Streamlining your operations may feel like a massive undertaking, but it is essential.

When to Choose Lean:
- Your focus is on quick, flexible manufacturing.
- Reduction of waste is a primary goal.
- You desire simplified processes without heavy reliance on data.
When to Choose Six Sigma:
- The priority is on stringent quality control and variance reduction.
- You’re prepared to invest in statistical training.
- Production processes significantly benefit from data analysis and precision.
Both strategies can be integrated for optimal performance, adding layers of efficiency and quality—key pointers that manufacturing settings value to deliver robust, reliable equipment.
For instance, a lean approach may suffice for a smaller business producing specialized attachments. Larger companies that manufacture a wider array of products might find the structure of Six Sigma more effective.

Integrating Lean and Six Sigma
Many companies find success by integrating Lean and Six Sigma, creating a powerful hybrid approach often known as Lean Six Sigma. This hybrid approach combines the speed of Lean with the meticulous quality control of Six Sigma, allowing manufacturers to deliver defect-free products rapidly. This gives them a significant competitive advantage.
- Integration Benefits:
- Operational Excellence: Streamlined processes and reduced defect rates.
- Data-Driven Improvements: Enhanced decision-making with added agility.
- Greater Competitiveness: Improved efficiency translates to greater market responsiveness.
As an example, let’s consider our self-dumping hoppers. Hopper manufacturing benefits from applying both Lean and Six Sigma. Lean principles help streamline the production line, minimizing waste and maximizing output. Six Sigma methodologies ensure the hoppers meet stringent safety standards, minimizing defects and guaranteeing reliability.

As outlined in our previous post, “Self-Dumping Hoppers: Everything You Need to Know,” our commitment to quality is evident in every product we manufacture.
Final Thoughts
Deciphering between Lean and Six Sigma doesn’t have to be daunting. Understanding your operational needs and strategic objectives enables you to make informed choices that propel your business toward success. With Lean’s efficiency and Six Sigma’s focus on quality, the integrated approach is a powerful blueprint to achieve excellence.
Implementing either Lean or Six Sigma requires careful planning. Resistance to change within your company culture is a common hurdle. Invest in adequate training, implement effective change management strategies, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Open communication is crucial.

Addressing these challenges head-on will ensure a smoother transition.
At Iron Bull Manufacturing, we are ready to help you adopt these methodologies. Contact us today to explore our range of products that make managing waste efficiently possible. Discover how our solutions can elevate your processes with safety, strength, and efficiency at the forefront.